Teen Pregnancy Statistics: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Teen pregnancy, defined as pregnancy in individuals under the age of 20, remains a significant public health concern worldwide. It is associated with numerous adverse outcomes for both the mother and child, including increased risks of premature birth, low birth weight, and infant mortality. Moreover, teen pregnancy can have profound social and economic consequences, contributing to poverty, educational disparities, and diminished future opportunities.
This article presents a comprehensive overview of teen pregnancy statistics in the United States, examining its prevalence, trends, and disparities across different demographic groups. By understanding these statistics, policymakers, healthcare providers, and community organizations can develop targeted interventions and strategies to address this critical issue.
Prevalence of Teen Pregnancy
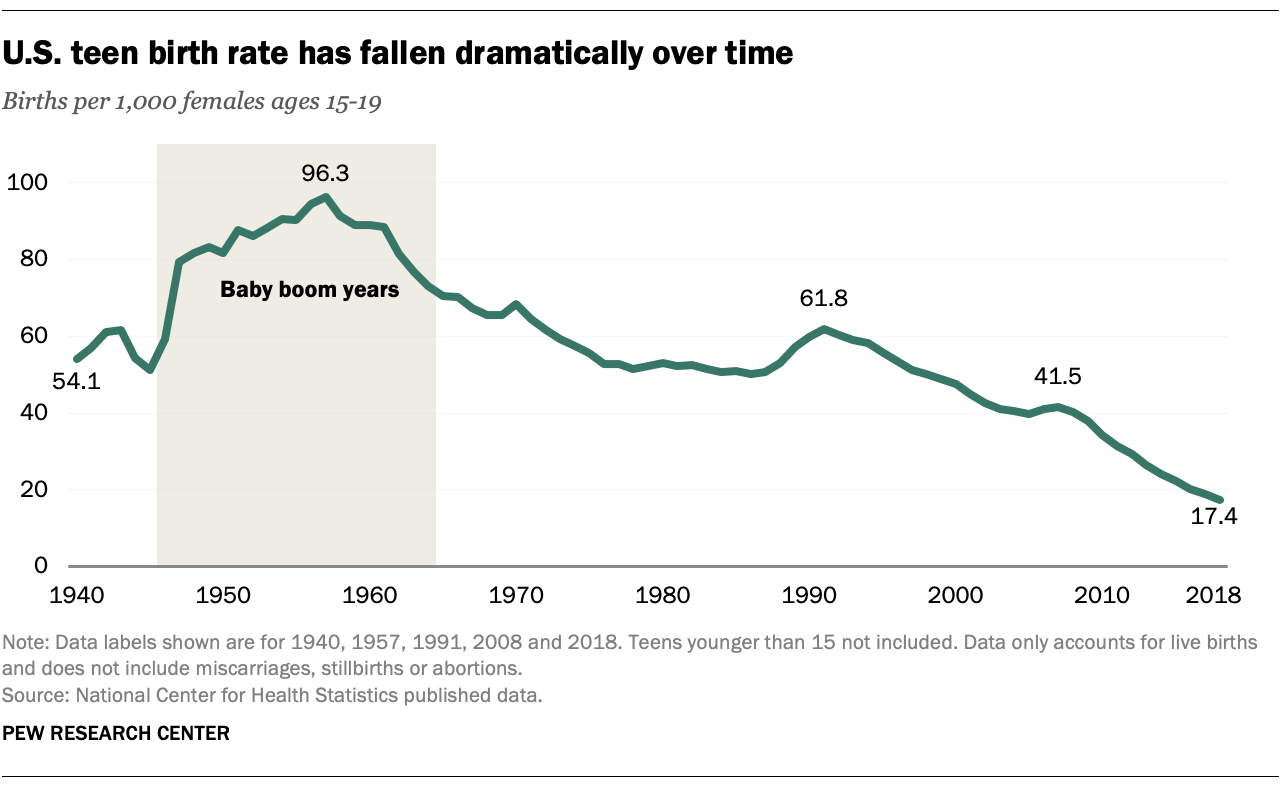
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the teen birth rate in the United States has declined significantly over the past several decades. In 2020, the birth rate among females aged 15-19 was 17.4 per 1,000, down from 26.5 per 1,000 in 2010. This decline is attributed to increased access to contraception, improved sex education, and greater awareness of the risks associated with teen pregnancy.
However, despite this progress, teen pregnancy remains a prevalent issue in certain populations. In 2020, the birth rate among Hispanic females aged 15-19 was 24.5 per 1,000, compared to 14.4 per 1,000 among non-Hispanic white females. Additionally, the birth rate among American Indian/Alaska Native females was 20.8 per 1,000, and among black females, it was 22.2 per 1,000.
Trends in Teen Pregnancy
The decline in the teen birth rate in the United States has been consistent over the past several decades. However, there have been some fluctuations in the rate, particularly among certain demographic groups. For example, the birth rate among Hispanic females has remained relatively stable in recent years, while the rate among black females has declined more slowly than the overall rate.
In addition to the overall decline in the teen birth rate, there has also been a shift in the age distribution of teen pregnancies. In 2020, the majority (62%) of teen births occurred among females aged 18-19, while only 38% occurred among females aged 15-17. This shift is likely due to increased access to contraception and improved sex education among younger teens.
Disparities in Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy rates vary significantly across different demographic groups. As mentioned earlier, Hispanic, American Indian/Alaska Native, and black females have higher birth rates than non-Hispanic white females. Additionally, there are disparities in teen pregnancy rates based on socioeconomic status, education level, and geographic location.
Females from low-income families are more likely to experience teen pregnancy than those from high-income families. Similarly, females who do not complete high school are more likely to become pregnant as teens than those who do. Furthermore, teen pregnancy rates are higher in rural areas than in urban areas.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy has numerous adverse consequences for both the mother and child. For the mother, teen pregnancy can increase the risk of premature birth, low birth weight, and infant mortality. It can also lead to complications during pregnancy and delivery, such as preeclampsia and eclampsia.
For the child, teen pregnancy can increase the risk of developmental delays, learning disabilities, and chronic health conditions. Children born to teen mothers are also more likely to experience poverty and educational disparities.
Social and Economic Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy can have profound social and economic consequences. Teen mothers are more likely to drop out of school, have lower earning potential, and experience poverty. They are also more likely to rely on public assistance programs.
The economic costs of teen pregnancy are substantial. In the United States, the estimated annual cost of teen pregnancy is over $9 billion. These costs include healthcare expenses, lost productivity, and increased social welfare spending.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, despite the progress that has been made in reducing the birth rate. Disparities in teen pregnancy rates persist across different demographic groups, and the consequences of teen pregnancy can be severe for both the mother and child.
Addressing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that includes increased access to contraception, improved sex education, and support for teen mothers and their children. By understanding the statistics and addressing the underlying factors that contribute to teen pregnancy, we can work towards reducing its prevalence and mitigating its negative consequences.