Prenatal Testing: A Comprehensive Guide to Tests Taken During Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a transformative journey that brings immense joy and anticipation. However, it also involves a series of tests and screenings designed to monitor the health of both the mother and the developing baby. These tests play a crucial role in detecting potential complications, ensuring a healthy pregnancy, and providing peace of mind to expectant parents.
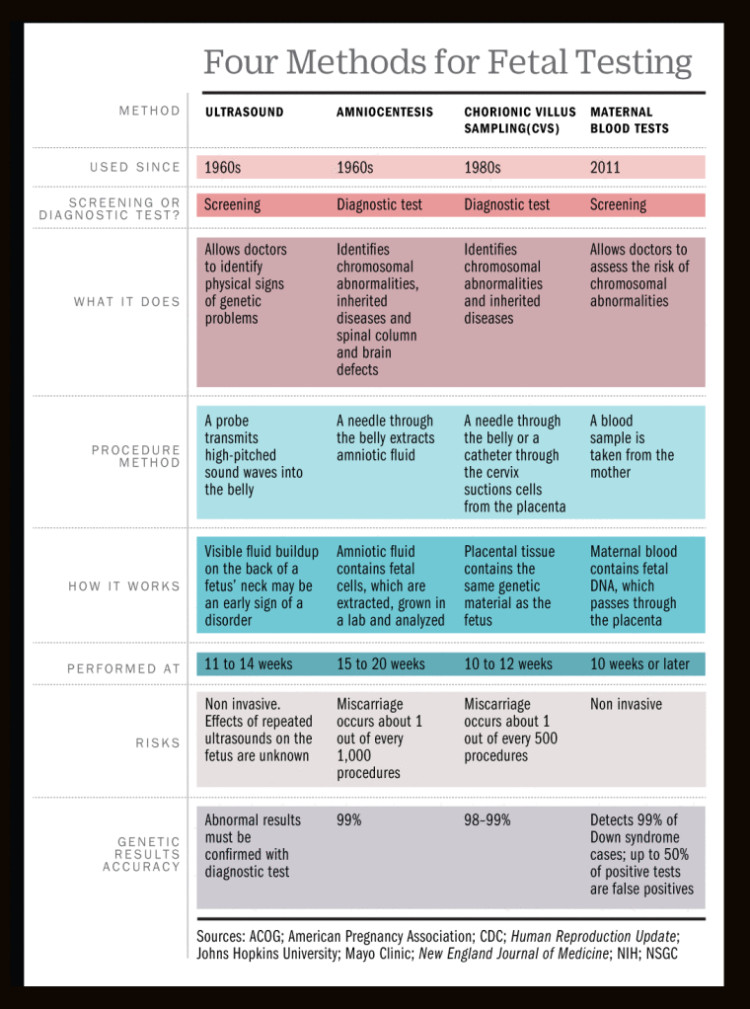
Types of Prenatal Tests
Prenatal tests can be categorized into two main types:
- Screening Tests: These tests assess the risk of certain birth defects or chromosomal abnormalities. They are typically non-invasive and have a low risk of complications.
- Diagnostic Tests: These tests provide a definitive diagnosis of a specific condition. They are more invasive and carry a higher risk of complications, but they can provide valuable information for decision-making.
Screening Tests
First Trimester Screening
- Nuchal Translucency (NT) Scan: An ultrasound that measures the fluid-filled space at the back of the baby’s neck. An increased NT measurement may indicate an increased risk of Down syndrome or other chromosomal abnormalities.
- Maternal Serum Screening: A blood test that measures levels of certain hormones and proteins. Abnormal levels may suggest an increased risk of Down syndrome or neural tube defects.
Second Trimester Screening
- Quadruple Screen: A blood test that measures levels of four hormones and proteins. It screens for Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and neural tube defects.
- Cell-Free Fetal DNA (cffDNA) Test: A blood test that analyzes fragments of fetal DNA circulating in the mother’s blood. It can detect Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13 with high accuracy.
Diagnostic Tests
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
- Procedure: A thin needle is inserted through the abdomen to collect a sample of chorionic villi, which are finger-like projections on the placenta.
- Timing: Performed between 10 and 13 weeks of pregnancy.
- Risks: Miscarriage (less than 1%), infection, bleeding.
- Results: Can detect chromosomal abnormalities, genetic disorders, and certain fetal infections.
Amniocentesis
- Procedure: A thin needle is inserted through the abdomen to collect a sample of amniotic fluid.
- Timing: Performed between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- Risks: Miscarriage (less than 1%), infection, bleeding, leakage of amniotic fluid.
- Results: Can detect chromosomal abnormalities, genetic disorders, neural tube defects, and fetal infections.
Ultrasound
- Procedure: High-frequency sound waves are used to create images of the baby and the uterus.
- Timing: Performed throughout pregnancy, but most commonly in the first and second trimesters.
- Risks: None.
- Results: Can assess fetal growth, anatomy, and development. Can also detect certain birth defects and complications.
Who Should Consider Prenatal Testing?
All pregnant women should consider prenatal screening tests, regardless of their age or risk factors. Diagnostic tests are typically recommended for women who:
- Are over 35 years old at the time of conception.
- Have a family history of birth defects or genetic disorders.
- Have had a previous child with a birth defect.
- Have abnormal results on screening tests.
Benefits of Prenatal Testing
- Early Detection: Prenatal tests can identify potential complications early in pregnancy, allowing for prompt intervention and management.
- Informed Decision-Making: The results of prenatal tests can help parents make informed decisions about their pregnancy and the future of their child.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that the baby is healthy or that any potential complications are being monitored can provide significant peace of mind to expectant parents.
Risks of Prenatal Testing
- False Positives: Screening tests can sometimes produce false positive results, indicating an increased risk of a condition that is not actually present.
- False Negatives: Screening tests can also produce false negative results, indicating a low risk of a condition that is actually present.
- Complications: Diagnostic tests carry a small risk of complications, such as miscarriage, infection, or bleeding.
Making a Decision
The decision of whether or not to undergo prenatal testing is a personal one. It is important to weigh the potential benefits and risks, as well as your own values and beliefs. Consult with your healthcare provider to discuss the options and make an informed decision that is right for you and your pregnancy.
Conclusion
Prenatal testing is an essential part of modern pregnancy care. By providing valuable information about the health of the mother and baby, these tests empower expectant parents to make informed decisions and ensure the best possible outcome for their child. While the decision of whether or not to undergo testing is a personal one, it is important to be aware of the options available and to discuss them thoroughly with your healthcare provider.