Teen Pregnancy: A Persistent Issue with Devastating Consequences
Introduction
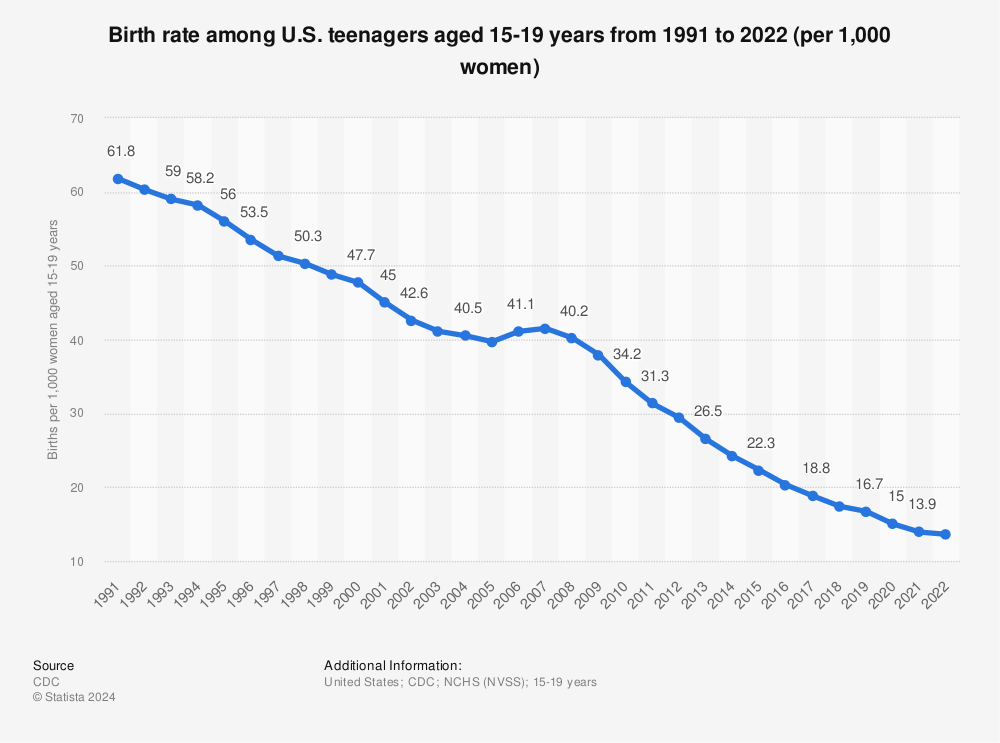
Teen pregnancy, defined as pregnancy occurring in individuals under the age of 20, remains a significant public health concern in the United States. Despite concerted efforts to reduce its prevalence, the yearly rates of teen pregnancy continue to be alarmingly high, with far-reaching consequences for both the young mothers and their children. This article delves into the complexities of teen pregnancy, examining its causes, consequences, and potential solutions.
Causes of Teen Pregnancy
The factors contributing to teen pregnancy are multifaceted and deeply rooted in social, economic, and cultural contexts. Some of the key causes include:
- Lack of comprehensive sex education: Many teens lack access to accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health and contraception. This knowledge gap can lead to risky sexual behavior and unplanned pregnancies.
- Peer pressure and social norms: Teenagers may engage in sexual activity to conform to peer expectations or to gain social status. In some communities, early childbearing is normalized, perpetuating the cycle of teen pregnancy.
- Poverty and lack of opportunities: Economic hardship and limited access to education and employment can contribute to teen pregnancy. Teens from disadvantaged backgrounds may view childbearing as a way to escape poverty or gain a sense of purpose.
- Trauma and abuse: A history of physical, emotional, or sexual abuse can increase the risk of teen pregnancy. Victims of abuse may seek sexual relationships as a coping mechanism or to gain a sense of control.
- Limited access to healthcare: Barriers to accessing affordable and confidential healthcare, including contraception and abortion services, can contribute to teen pregnancy.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy has profound consequences for both the young mothers and their children. These consequences include:
For the Young Mothers:
- Increased risk of health complications: Teen mothers are more likely to experience premature birth, low birth weight, and other pregnancy-related complications. They are also at higher risk for sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Lower educational attainment: Teen mothers are more likely to drop out of school, which can limit their future employment prospects and earning potential.
- Economic hardship: Teen mothers often face financial challenges, as they may have to balance childcare responsibilities with work or education.
- Social isolation: Teen mothers may experience stigma and judgment from their peers and community, leading to social isolation.
- Mental health issues: Teen mothers are at increased risk for depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems.
For the Children:
- Increased risk of health problems: Children born to teen mothers are more likely to have low birth weight, developmental delays, and other health issues.
- Lower educational attainment: Children of teen mothers are more likely to drop out of school and have lower educational achievement.
- Increased risk of poverty: Children of teen mothers are more likely to grow up in poverty, which can have long-term consequences for their health, education, and well-being.
- Intergenerational cycle of teen pregnancy: Children of teen mothers are more likely to become teen parents themselves, perpetuating the cycle of poverty and health disparities.
Solutions to Reduce Teen Pregnancy
Addressing the issue of teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that involves multiple stakeholders, including parents, educators, healthcare providers, and policymakers. Some potential solutions include:
- Improving access to comprehensive sex education: All teens should have access to medically accurate and age-appropriate sex education that covers topics such as contraception, STIs, and healthy relationships.
- Empowering teens with decision-making skills: Teens need to be equipped with the knowledge and skills to make informed decisions about their sexual health. This includes teaching them about contraception, consent, and the importance of healthy relationships.
- Providing access to affordable and confidential healthcare: Teens need access to affordable and confidential healthcare services, including contraception, STI testing and treatment, and abortion services.
- Addressing social and economic factors: Addressing the underlying social and economic factors that contribute to teen pregnancy, such as poverty, lack of opportunities, and trauma, is crucial. This includes providing support services, such as housing assistance, job training, and mental health counseling.
- Encouraging parental involvement: Parents play a vital role in preventing teen pregnancy. They can provide their children with guidance, support, and access to information about sexual health.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences for both the young mothers and their children. It is essential to address the underlying causes of teen pregnancy and implement comprehensive solutions that involve multiple stakeholders. By providing teens with access to comprehensive sex education, empowering them with decision-making skills, and addressing the social and economic factors that contribute to teen pregnancy, we can create a future where all young people have the opportunity to reach their full potential.