United States Average Teen Pregnancy in 2002: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, with far-reaching consequences for both the young mothers and their children. In 2002, the United States had one of the highest teen pregnancy rates among developed nations, with approximately 750,000 pregnancies occurring among girls aged 15-19. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the average teen pregnancy rate in the United States in 2002, examining its prevalence, contributing factors, and potential solutions.
Prevalence of Teen Pregnancy in 2002
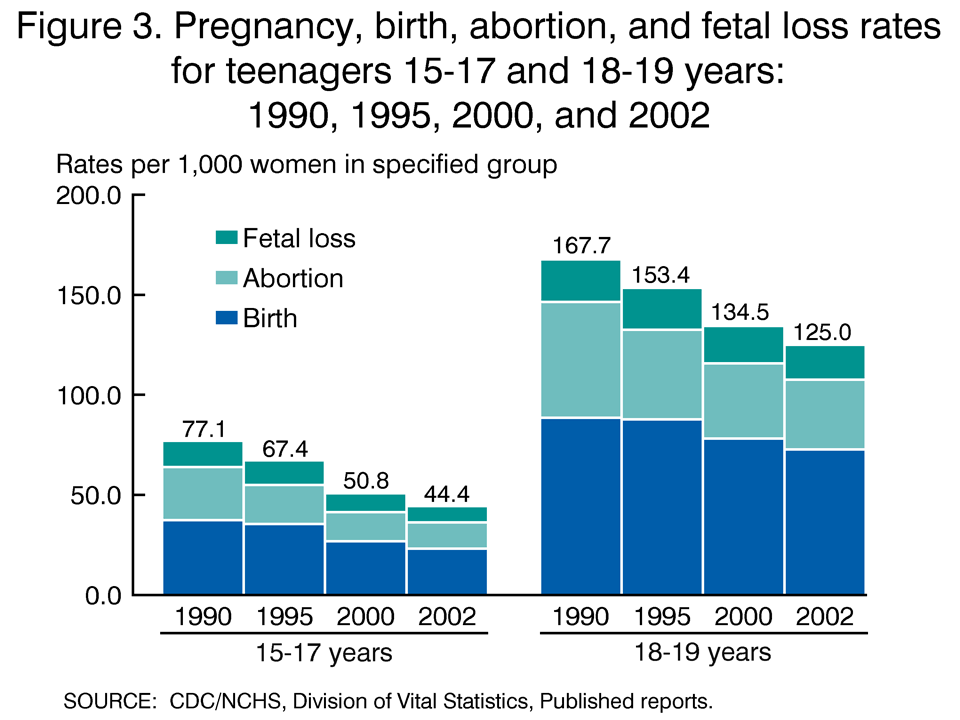
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the average teen pregnancy rate in the United States in 2002 was 41.9 pregnancies per 1,000 girls aged 15-19. This rate was significantly higher than the average rate of 26.5 pregnancies per 1,000 girls in developed countries. Among racial and ethnic groups, the teen pregnancy rate was highest among Hispanic girls (85.2 pregnancies per 1,000 girls), followed by African American girls (67.7 pregnancies per 1,000 girls) and white girls (34.3 pregnancies per 1,000 girls).
Contributing Factors to Teen Pregnancy
Numerous factors contribute to the high rate of teen pregnancy in the United States. These include:
- Poverty: Poverty is strongly correlated with teen pregnancy. Girls living in low-income households are more likely to experience early sexual activity, have unprotected sex, and lack access to comprehensive sex education and contraception.
- Lack of Education: Girls who drop out of school or have low educational attainment are at a higher risk of teen pregnancy. Education provides young women with the knowledge and skills necessary to make informed decisions about their sexual health.
- Peer Pressure: Teenagers who have friends who are sexually active are more likely to engage in sexual activity themselves. Peer pressure can influence young people’s attitudes and behaviors towards sex.
- Media Influences: The media often portrays teen pregnancy as glamorous or desirable, which can contribute to unrealistic expectations and normalize early sexual activity.
- Lack of Access to Contraception: Some teens lack access to affordable and confidential contraception, which increases their risk of unintended pregnancy.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy has significant consequences for both the young mothers and their children. These include:
- Health Risks: Teen mothers are at a higher risk of pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia, preterm labor, and low birth weight. Their children are also more likely to have health problems, including developmental delays and chronic diseases.
- Educational and Economic Challenges: Teen mothers are more likely to drop out of school and have lower educational attainment. They also face economic challenges, as they are less likely to have stable employment and earn higher incomes.
- Social Stigma: Teen mothers often face social stigma and discrimination, which can lead to isolation and depression.
Potential Solutions to Teen Pregnancy
Addressing the high rate of teen pregnancy in the United States requires a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Comprehensive Sex Education: Providing young people with comprehensive sex education, including information on contraception, sexually transmitted infections, and healthy relationships, is essential for reducing teen pregnancy.
- Increased Access to Contraception: Ensuring that teens have access to affordable and confidential contraception is crucial for preventing unintended pregnancy. This includes expanding access to birth control pills, condoms, and emergency contraception.
- Empowering Girls: Empowering girls through education, job training, and mentorship programs can help them make informed decisions about their sexual health and future.
- Reducing Poverty: Addressing poverty and its associated risk factors, such as lack of education and access to healthcare, can contribute to reducing teen pregnancy rates.
- Changing Social Norms: Changing social norms around teen pregnancy and promoting positive attitudes towards abstinence and responsible sexual behavior can help reduce the stigma associated with teen pregnancy and encourage young people to make healthy choices.
Conclusion
The average teen pregnancy rate in the United States in 2002 was 41.9 pregnancies per 1,000 girls aged 15-19. This rate was significantly higher than the average rate in developed countries and was particularly high among Hispanic and African American girls. Numerous factors contribute to teen pregnancy, including poverty, lack of education, peer pressure, media influences, and lack of access to contraception. Teen pregnancy has significant consequences for both the young mothers and their children, including health risks, educational and economic challenges, and social stigma. Addressing the high rate of teen pregnancy requires a multifaceted approach that includes comprehensive sex education, increased access to contraception, empowering girls, reducing poverty, and changing social norms. By implementing these solutions, the United States can reduce the number of teen pregnancies and improve the health and well-being of young people and their families.