Vaginal Bleeding During Pregnancy: Causes, Concerns, and Management
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is a common concern that affects approximately 20-30% of pregnant women. While it can be alarming, it’s important to remember that not all vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is a sign of a serious problem. However, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause and ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Causes of Vaginal Bleeding During Pregnancy
The causes of vaginal bleeding during pregnancy can vary depending on the stage of pregnancy.
First Trimester (Up to 12 Weeks)
- Implantation bleeding: Light bleeding or spotting can occur when the fertilized egg implants in the uterine lining, typically around 6-12 days after conception.
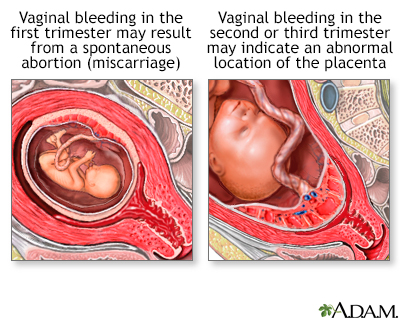
- Miscarriage: Heavy bleeding accompanied by cramping and pain can indicate a miscarriage.
- Ectopic pregnancy: Bleeding with severe pain in one side of the abdomen can be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus.
- Molar pregnancy: A rare condition where the placenta develops abnormally, causing vaginal bleeding and rapid uterine growth.
Second Trimester (13-27 Weeks)
- Placenta previa: Bleeding occurs when the placenta covers the cervix, causing the cervix to open prematurely.
- Placental abruption: Bleeding with abdominal pain can indicate placental abruption, where the placenta separates from the uterine wall.
- Uterine rupture: A rare but serious condition where the uterus tears open, causing severe bleeding and pain.
Third Trimester (28 Weeks to Delivery)
- Preterm labor: Bleeding with contractions can be a sign of preterm labor, where the baby is born before 37 weeks of gestation.
- Placental abruption: Similar to the second trimester, placental abruption can occur in the third trimester as well.
- Uterine rupture: This condition can also occur in the third trimester, especially if the uterus has been weakened by previous surgeries or pregnancies.
Other Causes
- Cervical polyps or cysts: These benign growths on the cervix can cause bleeding during pregnancy.
- Sex: Intercourse during pregnancy can sometimes cause minor bleeding due to irritation of the cervix.
- Trauma: Physical trauma to the abdomen or pelvis can lead to vaginal bleeding.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s important to seek medical attention promptly if you experience any vaginal bleeding during pregnancy, especially if it’s accompanied by any of the following symptoms:
- Heavy bleeding or bleeding that soaks through a pad in an hour
- Severe abdominal pain or cramping
- Fever or chills
- Dizziness or fainting
- Discharge with a foul odor
Diagnosis and Management
Upon presentation to the healthcare provider, they will perform a physical examination and ask about your symptoms and medical history. They may also order tests such as:
- Ultrasound: To visualize the uterus, placenta, and baby
- Blood tests: To check for anemia or infection
- Cervical exam: To examine the cervix for any abnormalities
The management of vaginal bleeding during pregnancy depends on the underlying cause.
- Implantation bleeding: Usually resolves on its own and does not require treatment.
- Miscarriage: May require medical intervention, such as medication or surgery.
- Ectopic pregnancy: Requires immediate surgical intervention.
- Placenta previa: May require bed rest, medication, or surgery to prevent further bleeding.
- Placental abruption: Requires immediate hospitalization and may involve delivery of the baby.
- Uterine rupture: Requires emergency surgery.
Prevention
While not all causes of vaginal bleeding during pregnancy can be prevented, there are some measures you can take to reduce your risk:
- Avoid strenuous activity or heavy lifting.
- Get regular prenatal care to monitor your pregnancy and identify any potential problems early on.
- Manage underlying medical conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Practice safe sex to prevent sexually transmitted infections.
Conclusion
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy can be a concerning symptom, but it’s important to remember that it’s not always a sign of a serious problem. By seeking medical attention promptly, you can ensure the timely diagnosis and appropriate management of the underlying cause, safeguarding the well-being of both you and your baby. Regular prenatal care, healthy lifestyle choices, and awareness of the potential causes and symptoms of vaginal bleeding can help reduce your risk and ensure a healthy pregnancy.