Week by Week Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
Pregnancy is an extraordinary journey that brings immense joy and anticipation. As your body undergoes remarkable transformations to nurture a new life, it’s essential to understand the developmental milestones and changes that occur each week. This week-by-week pregnancy guide provides a detailed overview of the physical, emotional, and fetal development during the entire 40-week gestation period.
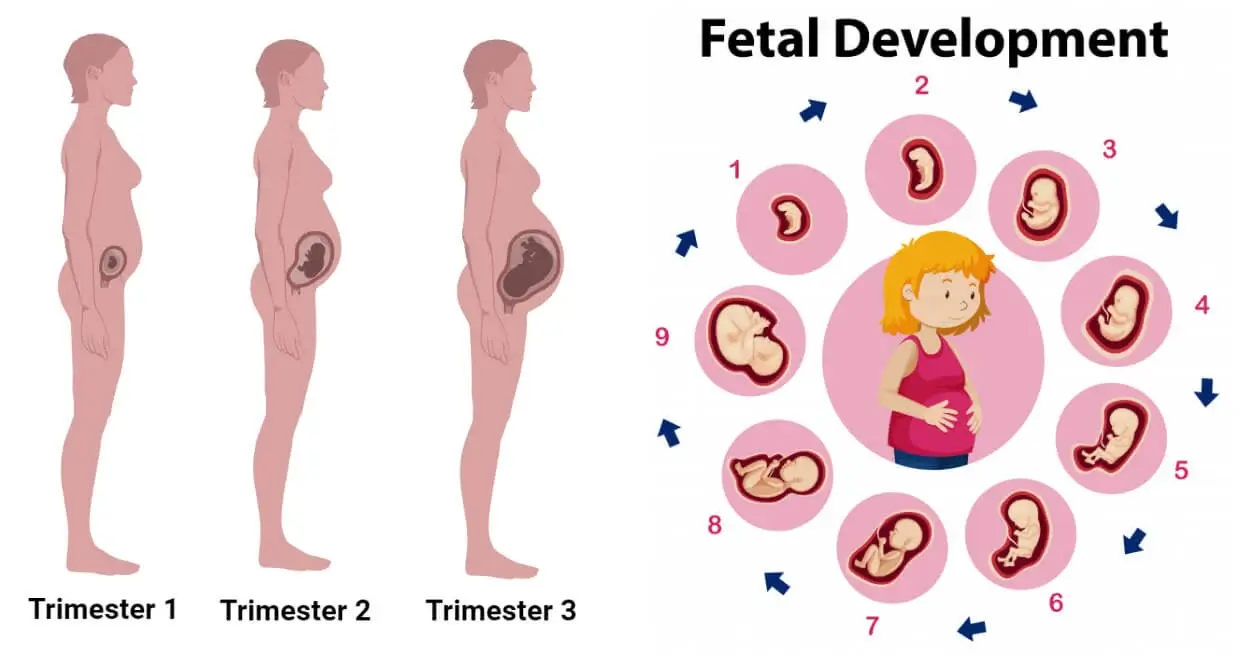
Week 1-4: The Beginning of Life
- Conception: Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell meets an egg cell, creating a single-celled zygote.
- Implantation: The zygote travels through the fallopian tube and implants into the uterine lining, becoming an embryo.
- Embryonic Development: The embryo begins to develop three distinct layers that will eventually form the body’s organs and tissues.
Week 5-8: Embryonic Development and Early Symptoms
- Embryonic Growth: The embryo grows rapidly, forming the neural tube, heart, and other vital organs.
- Early Pregnancy Symptoms: Fatigue, nausea, and breast tenderness may become noticeable.
- Ultrasound: A transvaginal ultrasound may be performed to confirm pregnancy and assess fetal development.
Week 9-12: Fetal Development and Organ Formation
- Fetal Development: The embryo is now referred to as a fetus, and its major organs begin to function.
- Organ Formation: The fetus’s limbs, fingers, toes, and facial features become more defined.
- Nuchal Translucency Screening: A blood test and ultrasound may be used to screen for chromosomal abnormalities.
Week 13-16: Fetal Growth and Movement
- Fetal Growth: The fetus grows significantly, and its movements become more noticeable.
- Quickening: Many women feel their baby’s movements for the first time around this time.
- Gender Determination: An ultrasound may be performed to determine the baby’s gender.
Week 17-20: Fetal Development and Maternal Changes
- Fetal Development: The fetus’s eyes open, and its hair and nails begin to grow.
- Maternal Changes: The uterus expands, and the baby bump becomes more prominent.
- Anatomy Scan: A detailed ultrasound is performed to assess the baby’s anatomy and growth.
Week 21-24: Fetal Growth and Sensory Development
- Fetal Growth: The fetus gains weight and its skin becomes less transparent.
- Sensory Development: The fetus begins to hear and respond to sounds.
- Gestational Diabetes Screening: A glucose tolerance test may be performed to screen for gestational diabetes.
Week 25-28: Fetal Movement and Breathing
- Fetal Movement: The fetus’s movements become more frequent and powerful.
- Breathing: The fetus begins to practice breathing movements.
- Fetal Position: The fetus may turn head-down in preparation for birth.
Week 29-32: Fetal Growth and Lung Development
- Fetal Growth: The fetus continues to grow rapidly, and its lungs mature.
- Lung Development: The fetus’s lungs produce surfactant, a substance that helps them expand with air.
- Biophysical Profile: An ultrasound and fetal heart rate monitoring may be performed to assess fetal well-being.
Week 33-36: Fetal Development and Weight Gain
- Fetal Development: The fetus’s brain and nervous system continue to develop.
- Weight Gain: The fetus gains significant weight and its body becomes rounder.
- Antepartum Fetal Monitoring: Regular checkups and fetal heart rate monitoring may be performed to ensure fetal well-being.
Week 37-40: Preparing for Birth
- Fetal Development: The fetus’s lungs are fully mature, and it prepares for birth.
- Labor and Delivery: Labor contractions begin, and the baby is born.
- Postpartum Care: After birth, the mother and baby receive medical care and support.
Emotional and Physical Changes During Pregnancy
In addition to the physical changes, pregnancy also brings about significant emotional and psychological changes.
- Mood Swings: Hormonal fluctuations can lead to mood swings, irritability, and anxiety.
- Fatigue: Increased progesterone levels can cause fatigue and drowsiness.
- Increased Appetite: The body requires more nutrients during pregnancy, leading to increased appetite.
- Constipation: Progesterone can slow down digestion, causing constipation.
- Frequent Urination: The growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder, increasing the frequency of urination.
Tips for a Healthy Pregnancy
- Prenatal Care: Attend regular prenatal appointments to monitor fetal development and your health.
- Nutrition: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise: Engage in moderate-intensity exercise as recommended by your doctor.
- Sleep: Get plenty of rest and establish a regular sleep schedule.
- Stress Management: Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Avoid Alcohol and Smoking: These substances can harm the developing fetus.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids, especially water.
Conclusion
Pregnancy is a remarkable journey that involves both physical and emotional transformations. By understanding the week-by-week development of your baby and your body, you can navigate this journey with confidence and excitement. Remember to seek regular prenatal care, follow a healthy lifestyle, and embrace the support of loved ones. As you approach the birth of your little one, know that you are embarking on a new chapter filled with love, joy, and the unbreakable bond between a mother and her child.