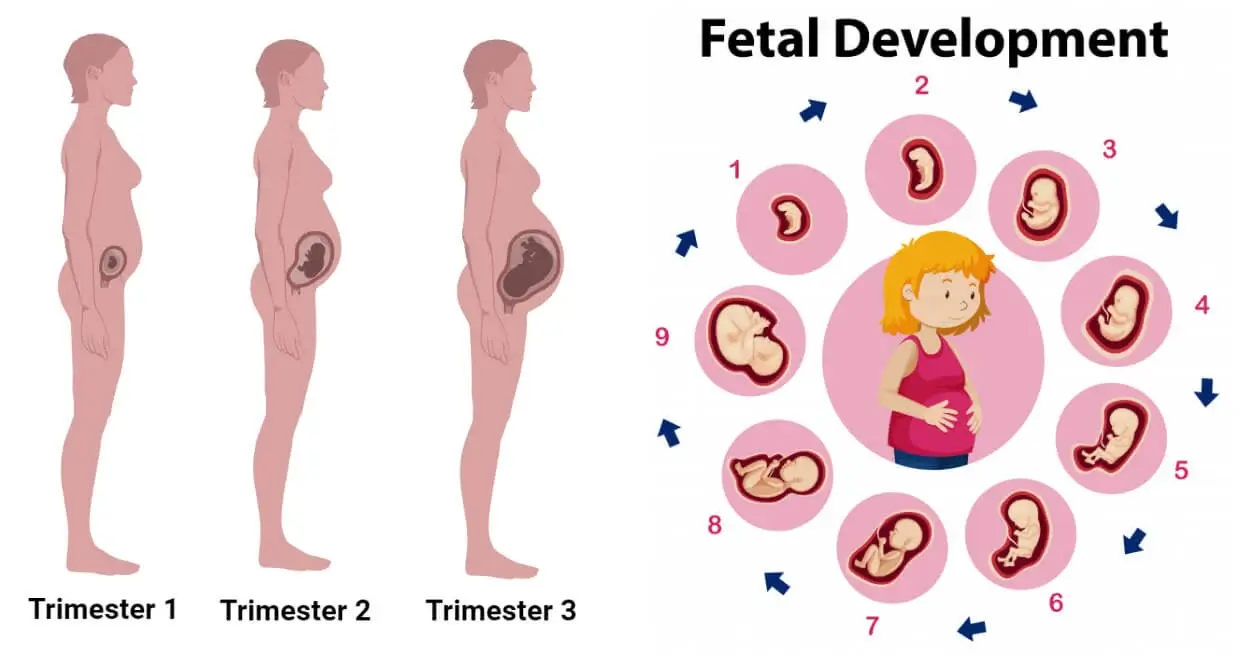
Week by Week Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
Pregnancy is an extraordinary journey that brings forth a myriad of physical, emotional, and hormonal changes. Understanding these changes week by week can help expectant mothers navigate this transformative experience with confidence and ease. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key milestones and developments that occur during each week of pregnancy.
Week 1-2: Conception and Implantation
- Conception occurs when a sperm fertilizes an egg in the fallopian tube.
- The fertilized egg, known as a zygote, travels through the fallopian tube towards the uterus.
- Around day 6-7, the zygote undergoes rapid cell division and becomes a blastocyst.
- The blastocyst implants into the uterine lining, marking the beginning of pregnancy.
Week 3-4: Embryonic Development
- The blastocyst differentiates into two layers: the inner cell mass and the trophoblast.
- The inner cell mass will eventually form the embryo, while the trophoblast will develop into the placenta.
- The embryo begins to form basic structures, including the neural tube and the heart.
Week 5-6: Organogenesis
- The embryo undergoes rapid growth and development, forming major organs and systems.
- The heart begins to beat, and the limbs and facial features start to take shape.
- The placenta becomes fully functional, providing oxygen and nutrients to the developing embryo.
Week 7-8: Fetal Development
- The embryo is now referred to as a fetus.
- The fetus grows rapidly, and the external genitalia become visible.
- The fetus begins to make small movements, such as kicking and stretching.
Week 9-12: Growth and Refinement
- The fetus continues to grow and develop, with the limbs becoming more defined.
- The fingers and toes become visible, and the fetus starts to develop fingernails and toenails.
- The fetus begins to produce urine and feces.
Week 13-16: Gender Determination
- By week 13, the external genitalia are fully formed, allowing for gender determination through ultrasound.
- The fetus continues to grow and develop, with the skin becoming thicker and the hair starting to grow.
- The fetus begins to respond to sounds and light.
Week 17-20: Movement and Growth
- The fetus becomes more active, with increased movement and kicking.
- The fetus begins to practice breathing and swallowing.
- The fetus grows rapidly, and the mother’s belly starts to show.
Week 21-24: Sensory Development
- The fetus’s senses begin to develop, including hearing, sight, and taste.
- The fetus can now distinguish between light and dark and respond to sounds.
- The fetus begins to develop a sleep-wake cycle.
Week 25-28: Rapid Growth
- The fetus grows rapidly, gaining weight and developing fat.
- The lungs continue to mature, and the fetus begins to produce surfactant, a substance that helps the lungs expand.
- The fetus’s skin becomes smoother and less wrinkled.
Week 29-32: Brain Development
- The fetus’s brain undergoes significant development, with increased brain activity and the formation of new neural connections.
- The fetus can now recognize familiar voices and sounds.
- The fetus’s reflexes become more coordinated.
Week 33-36: Preparing for Birth
- The fetus’s head becomes engaged in the pelvis, preparing for birth.
- The fetus gains weight and develops a protective layer of vernix caseosa on its skin.
- The fetus’s lungs are fully mature, and it is capable of breathing independently.
Week 37-40: Final Preparations
- The fetus continues to gain weight and prepare for birth.
- The cervix begins to soften and dilate in preparation for labor.
- The fetus’s movements may decrease as it runs out of space in the uterus.
Week 41+: Post-Term Pregnancy**
- If the baby is not born by week 41, it is considered post-term.
- The placenta may begin to deteriorate, reducing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the baby.
- The doctor may recommend induction or a cesarean section to ensure the baby’s safety.
Physical Changes During Pregnancy
In addition to the fetal development milestones, pregnancy brings about a range of physical changes in the mother’s body:
- Breast enlargement: Breasts begin to prepare for breastfeeding by increasing in size and tenderness.
- Nausea and vomiting: Morning sickness is a common symptom in the first trimester due to hormonal changes.
- Fatigue: Increased progesterone levels can lead to fatigue and drowsiness.
- Frequent urination: As the uterus expands, it puts pressure on the bladder, increasing the need to urinate.
- Abdominal pain: Round ligament pain, caused by the stretching of ligaments supporting the uterus, is common in the second and third trimesters.
- Constipation: Progesterone slows down digestion, leading to constipation.
- Hemorrhoids: Increased blood flow to the pelvic area can cause hemorrhoids, which are swollen veins in the rectum.
- Varicose veins: Increased blood volume and pressure can lead to varicose veins, which are swollen and twisted veins in the legs.
- Stretch marks: As the skin stretches to accommodate the growing uterus, stretch marks may appear on the abdomen, breasts, and thighs.
Emotional Changes During Pregnancy
Pregnancy also brings about a range of emotional changes, including:
- Mood swings: Hormonal changes can cause mood swings, from elation to irritability.
- Anxiety: Concerns about the pregnancy, labor, and the baby’s health can lead to anxiety.
- Depression: Some women experience prenatal depression, which can be caused by hormonal changes or underlying mental health conditions.
- Increased libido: In some women, increased blood flow to the pelvic area can lead to increased libido.
- Nesting: In the third trimester, some women experience a surge of energy and a desire to prepare for the baby’s arrival.
Prenatal Care
Regular prenatal care is essential for ensuring the health of both the mother and the baby. Prenatal appointments typically include:
- Physical exams: To monitor the mother’s weight, blood pressure, and overall health.
- Ultrasound exams: To assess the baby’s growth, development, and position.
- Blood tests: To check for anemia, infections, and other health conditions.
- Urine tests: To check for protein, glucose, and other substances that may indicate health problems.
- Education and counseling: To provide information about pregnancy, labor, and parenting.
Conclusion
Pregnancy is a transformative journey that involves both physical and emotional changes. Understanding the week-by-week milestones and developments can help expectant mothers navigate this experience with confidence and ease. Regular prenatal care is essential for ensuring the health of both the mother and the baby. By embracing the changes and seeking support when needed, women can enjoy a fulfilling and memorable pregnancy.