What to Eat During Pregnancy: A Comprehensive Guide
Pregnancy is a transformative journey that requires careful attention to nutrition. Eating a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing baby. This comprehensive guide will provide expectant mothers with a detailed overview of what to eat during pregnancy, addressing key nutrient needs, food safety considerations, and dietary recommendations.
Nutritional Needs During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the body’s nutritional requirements increase significantly. Some of the most important nutrients for expectant mothers include:
- Folic Acid: Essential for preventing neural tube defects in the baby.
- Iron: Necessary for red blood cell production and oxygen delivery to the baby.
- Calcium: Crucial for bone development and maternal bone health.
- Protein: Building blocks for the baby’s tissues and organs.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Support brain and eye development in the baby.
- Vitamin D: Aids in calcium absorption and bone health.
- Iodine: Essential for thyroid hormone production, which is vital for fetal brain development.
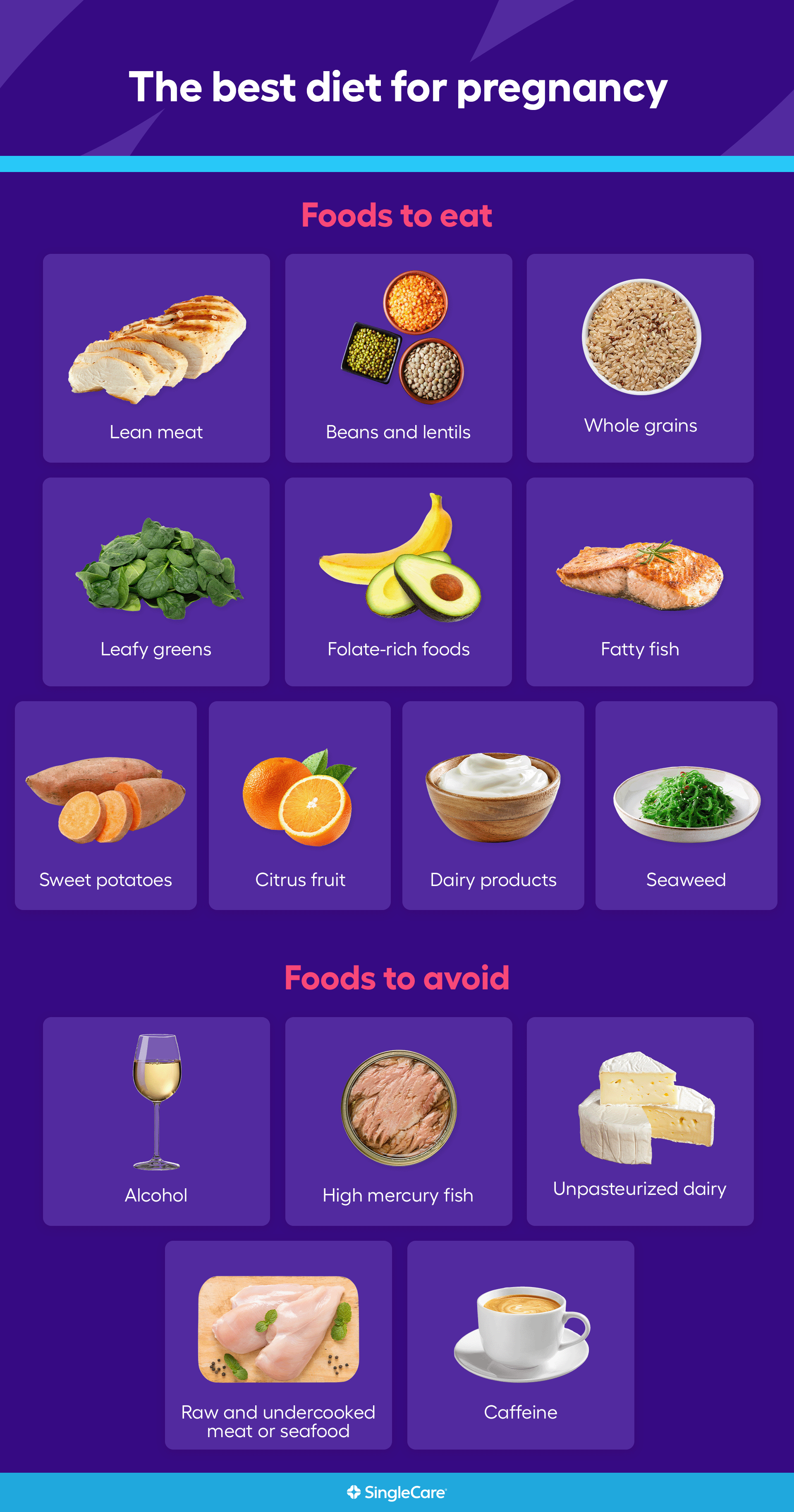
Food Groups to Focus On
To meet these increased nutritional needs, expectant mothers should focus on consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods from all food groups:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. Aim for at least 5 servings per day.
- Whole Grains: Provide fiber, B vitamins, and iron. Include whole-wheat bread, brown rice, and oatmeal in your diet.
- Lean Protein: Essential for building and repairing tissues. Choose lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, and lentils.
- Dairy Products: Excellent sources of calcium, protein, and vitamin D. Opt for low-fat or fat-free milk, yogurt, and cheese.
- Healthy Fats: Provide energy and support brain development. Include olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds in your meals.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
While most foods are safe to consume during pregnancy, there are certain foods that should be limited or avoided due to potential risks:
- Raw or Undercooked Meat, Poultry, and Fish: Can contain harmful bacteria or parasites.
- Unpasteurized Milk and Cheese: May contain bacteria that can cause foodborne illnesses.
- Raw or Undercooked Eggs: Can carry salmonella bacteria.
- High-Mercury Fish: Limit consumption of fish high in mercury, such as shark, swordfish, and king mackerel.
- Alcohol: Can cross the placenta and harm the baby.
- Caffeine: Excessive caffeine intake may increase the risk of miscarriage and low birth weight.
Food Safety Considerations
Ensuring food safety is paramount during pregnancy to protect both the mother and the baby from foodborne illnesses:
- Wash Fruits and Vegetables Thoroughly: Remove dirt and bacteria by washing produce under running water before eating.
- Cook Meat and Fish to a Safe Internal Temperature: Use a food thermometer to ensure meats and fish are cooked to the recommended internal temperature to kill harmful bacteria.
- Avoid Cross-Contamination: Keep raw meat, poultry, and fish separate from other foods to prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Refrigerate Perishable Foods Promptly: Keep perishable foods cold to prevent bacterial growth.
Dietary Recommendations
The following dietary recommendations provide a general framework for healthy eating during pregnancy:
- Calories: Aim for an additional 340-450 calories per day during the second trimester and 450-500 calories per day during the third trimester.
- Protein: Increase protein intake to 71 grams per day.
- Iron: Aim for 27 milligrams of iron per day.
- Calcium: Consume 1,000 milligrams of calcium per day.
- Folic Acid: Take a prenatal vitamin containing 600 micrograms of folic acid daily.
Special Dietary Considerations
Certain medical conditions or dietary preferences may require modifications to the general dietary recommendations. For example:
- Gestational Diabetes: Expectant mothers with gestational diabetes may need to follow a specific diet to manage blood sugar levels.
- Vegetarian or Vegan Diets: Vegetarians and vegans may need to pay extra attention to getting enough protein, iron, and vitamin B12.
- Food Allergies: Women with food allergies should avoid consuming foods that trigger their allergies.
Monitoring and Support
Regular prenatal checkups with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring the mother’s health and nutritional status. The provider can provide personalized dietary advice, address any concerns, and recommend prenatal vitamins or supplements as needed.
Conclusion
Eating a balanced and nutritious diet during pregnancy is crucial for the well-being of both the mother and the baby. By understanding the increased nutritional needs, focusing on nutrient-rich foods, limiting or avoiding certain foods, ensuring food safety, and following dietary recommendations, expectant mothers can optimize their nutrition and support the healthy development of their child. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and to address any specific dietary concerns or restrictions.