2000 Teen Pregnancy Statistics: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, with far-reaching implications for both the young mothers and their children. This comprehensive analysis delves into the latest statistics on teen pregnancy, examining trends, disparities, and the impact on society.
National Overview
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the teen birth rate in the United States has declined steadily in recent decades. In 2000, there were an estimated 496,682 teen births, a rate of 46.5 per 1,000 females aged 15-19. This represented a 17% decrease from the peak rate of 56.3 in 1991.
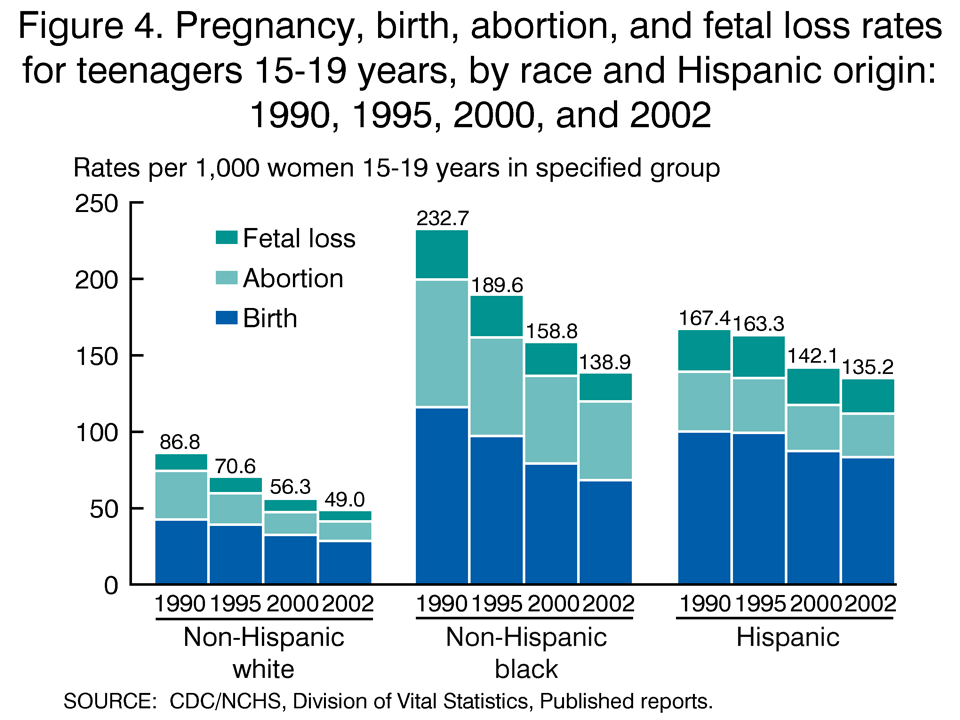
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Despite the overall decline, racial and ethnic disparities in teen pregnancy rates persist. In 2000, the teen birth rate for non-Hispanic Black females was 89.3 per 1,000, more than twice the rate for non-Hispanic White females (33.2). Hispanic females also had a higher rate (56.6) than White females.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors play a significant role in teen pregnancy rates. Teenagers living in poverty or near poverty are more likely to become pregnant than those from more affluent backgrounds. In 2000, the teen birth rate for females living below the poverty level was 106.8 per 1,000, compared to 28.5 for females living above the poverty level.
Education
Education is another key factor associated with teen pregnancy. Teenagers who drop out of school are more likely to become pregnant than those who graduate. In 2000, the teen birth rate for high school dropouts was 100.9 per 1,000, compared to 32.2 for high school graduates.
Consequences for Teen Mothers
Teen pregnancy has numerous negative consequences for the young mothers. They are more likely to drop out of school, have lower incomes, and experience poverty. They also face higher risks of health problems, such as preterm birth and low birth weight.
Consequences for Children of Teen Mothers
Children born to teen mothers also face challenges. They are more likely to be born prematurely, have low birth weight, and experience developmental delays. They are also more likely to live in poverty and drop out of school.
Economic Impact
Teen pregnancy has a significant economic impact on society. The estimated cost of teen pregnancy in the United States in 2000 was $9.4 billion. This includes the costs of medical care, education, and lost productivity.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying factors that contribute to it. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing teenagers with accurate information about sex and contraception is essential for preventing unplanned pregnancies.
- Access to contraception: Making contraception easily accessible to teenagers is crucial for reducing unintended pregnancies.
- Economic support: Providing economic support to low-income teenagers can help them stay in school and avoid the risks associated with teen pregnancy.
- Mentoring and support programs: Mentoring and support programs can provide teenagers with the guidance and support they need to make healthy choices.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, with far-reaching consequences for both the young mothers and their children. Addressing the underlying factors that contribute to teen pregnancy, such as poverty, lack of education, and limited access to contraception, is essential for reducing the teen birth rate and improving the lives of young people.