Ovarian Cysts and Ectopic Pregnancies: Understanding the Differences
Introduction
Ovarian cysts and ectopic pregnancies are two common gynecological conditions that can affect women of reproductive age. While both conditions can cause pain and other symptoms, they are distinct in their causes, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding the differences between these two conditions is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate management.
Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or within the ovaries. They are common, affecting up to 20% of women at some point in their lives. Most ovarian cysts are benign (non-cancerous) and resolve on their own without treatment. However, some cysts can become large or cause complications, requiring medical or surgical intervention.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
- Functional cysts: These are the most common type of ovarian cyst and usually form during the menstrual cycle. They typically resolve within a few months.
- Dermoid cysts: These cysts contain various tissues, such as hair, skin, or teeth. They are usually benign but can grow large and require surgery.
- Endometriomas: These cysts are associated with endometriosis, a condition where uterine tissue grows outside the uterus. They can be painful and may affect fertility.
- Cystadenomas: These cysts are filled with fluid or mucus and can become quite large. They are usually benign but may require surgery if they cause symptoms.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
Most ovarian cysts do not cause any symptoms. However, larger cysts or those that rupture can cause:
- Pelvic pain
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Bloating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty urinating or defecating
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cysts
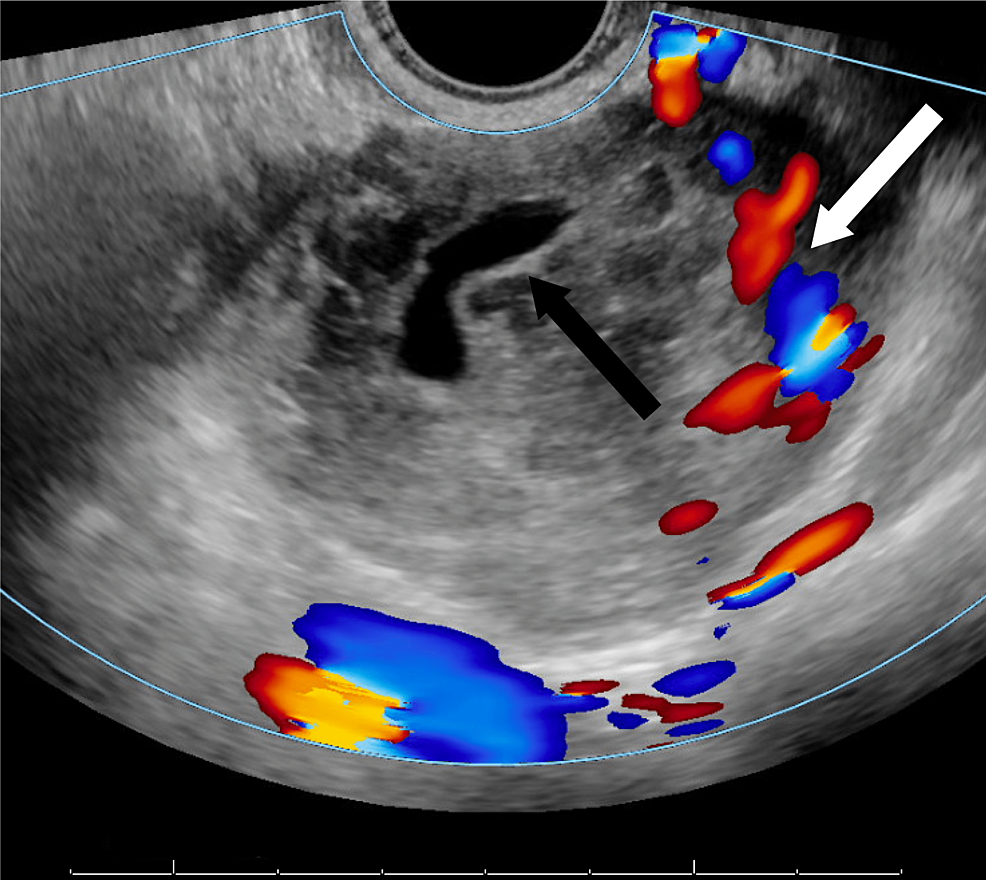
Ovarian cysts are typically diagnosed through a pelvic exam and ultrasound. The ultrasound can visualize the cyst and determine its size, location, and characteristics. Blood tests may also be ordered to rule out other conditions.
Treatment of Ovarian Cysts
Most small, asymptomatic ovarian cysts do not require treatment. However, larger cysts or those that cause symptoms may require:
- Observation: Small cysts may be monitored with regular ultrasounds to ensure they are not growing or causing problems.
- Medication: Hormonal medications can help shrink functional cysts.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the cyst may be necessary if it is large, causing symptoms, or suspected to be cancerous.
Ectopic Pregnancies
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube. Ectopic pregnancies are life-threatening emergencies and require immediate medical attention.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancies
The exact cause of ectopic pregnancies is often unknown. However, certain factors can increase the risk, including:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Endometriosis
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
- Use of intrauterine devices (IUDs)
- Smoking
- Infertility treatments
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancies
Ectopic pregnancies can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Pelvic pain
- Irregular vaginal bleeding
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness or fainting
- Shoulder pain (if the ectopic pregnancy ruptures)
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancies
Ectopic pregnancies are diagnosed through a combination of symptoms, physical exam, and ultrasound. Blood tests may also be ordered to measure hormone levels.
Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancies
Ectopic pregnancies cannot be carried to term and require immediate treatment to prevent life-threatening complications. Treatment options include:
- Medication: Methotrexate, a chemotherapy drug, can be used to terminate the pregnancy and dissolve the ectopic tissue.
- Surgery: Laparoscopic or open surgery may be necessary to remove the ectopic pregnancy and repair the affected fallopian tube.
Complications of Ovarian Cysts and Ectopic Pregnancies
Ovarian Cysts
- Ovarian torsion (twisting of the ovary)
- Rupture of the cyst
- Infertility (in rare cases)
Ectopic Pregnancies
- Ruptured ectopic pregnancy (life-threatening)
- Internal bleeding
- Infection
- Infertility (if the fallopian tube is damaged)
Prevention of Ovarian Cysts and Ectopic Pregnancies
There is no sure way to prevent ovarian cysts or ectopic pregnancies. However, certain measures may reduce the risk:
- Regular pelvic exams
- Early diagnosis and treatment of pelvic infections
- Use of barrier contraception (condoms)
- Quitting smoking
- Avoiding infertility treatments that increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy
Conclusion
Ovarian cysts and ectopic pregnancies are two distinct gynecological conditions with different causes, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding the differences between these conditions is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate management. Early detection and treatment can prevent serious complications and improve outcomes for women.