Ovarian Cyst Pregnancy: A Rare and Complex Condition
Introduction
Pregnancy is a remarkable physiological process that typically occurs within the uterine cavity. However, in rare cases, pregnancy can develop outside the uterus, known as an ectopic pregnancy. One such type of ectopic pregnancy is an ovarian cyst pregnancy, where the fertilized egg implants within an ovarian cyst. This condition is exceedingly uncommon, accounting for approximately 1-3% of all ectopic pregnancies.
Pathophysiology
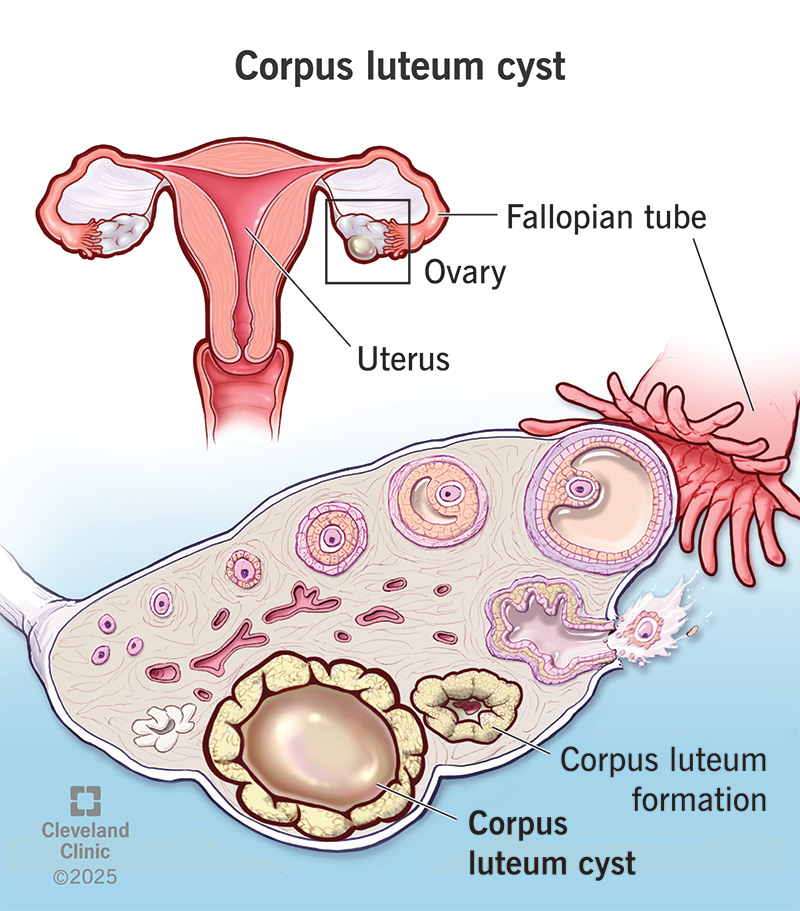
Ovarian cyst pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants within a pre-existing ovarian cyst. The cyst may be functional, such as a follicular or corpus luteum cyst, or non-functional, such as a dermoid or endometriotic cyst. The exact mechanism of implantation is not fully understood, but it is believed that the cyst wall provides a suitable environment for embryonic development.
Clinical Presentation
The clinical presentation of an ovarian cyst pregnancy can vary widely. Some women may experience symptoms similar to a normal intrauterine pregnancy, such as amenorrhea, breast tenderness, and nausea. However, others may present with more specific symptoms, including:
- Pelvic pain, which can range from mild to severe
- Irregular vaginal bleeding
- Abdominal distension
- Urinary frequency or urgency
- Gastrointestinal symptoms, such as constipation or diarrhea
Diagnosis
Diagnosing an ovarian cyst pregnancy can be challenging, as the symptoms often overlap with those of other conditions. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential. Transvaginal ultrasound is the primary imaging modality used to confirm the diagnosis. Ultrasound findings suggestive of an ovarian cyst pregnancy include:
- An intracystic gestational sac
- A fetal pole with cardiac activity
- Increased vascularity within the cyst wall
Differential Diagnosis
Several other conditions can mimic the clinical presentation of an ovarian cyst pregnancy, including:
- Ruptured ovarian cyst
- Corpus luteum cyst
- Hydrosalpinx
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Endometriosis
Management
The management of an ovarian cyst pregnancy depends on the size and location of the cyst, the gestational age of the embryo, and the patient’s overall health. Treatment options include:
Conservative Management:
- Close monitoring with serial ultrasound examinations
- Hormonal therapy to suppress ovarian function and promote cyst regression
- Aspiration of the cyst under ultrasound guidance
Surgical Management:
- Laparoscopic or open surgery to remove the cyst and the developing embryo
- Oophorectomy (removal of the ovary) may be necessary in some cases
Prognosis
The prognosis for an ovarian cyst pregnancy is generally good, with most women experiencing a successful outcome. However, the risk of complications, such as cyst rupture or hemorrhage, is higher compared to intrauterine pregnancies.
Complications
Potential complications of an ovarian cyst pregnancy include:
- Cyst rupture, which can lead to internal bleeding and pain
- Hemorrhage, which can be life-threatening
- Infection
- Infertility
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent an ovarian cyst pregnancy. However, early detection and prompt treatment can minimize the risk of complications. Women with a history of ovarian cysts or ectopic pregnancies should be closely monitored during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Ovarian cyst pregnancy is a rare and complex condition that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate management. While the prognosis is generally good, it is important to be aware of the potential complications and to seek medical attention promptly if any symptoms suggestive of an ovarian cyst pregnancy arise.