Teen Pregnancy: A Statistical Analysis
Teen pregnancy, defined as pregnancy in females under the age of 20, remains a significant public health concern in the United States. Despite a steady decline in teen birth rates over the past few decades, the issue continues to disproportionately affect certain populations, highlighting the need for targeted interventions and comprehensive support systems. This article delves into the statistics surrounding teen pregnancy in the United States, examining trends, risk factors, and the impact on both the teenage mother and the child.
Prevalence and Trends
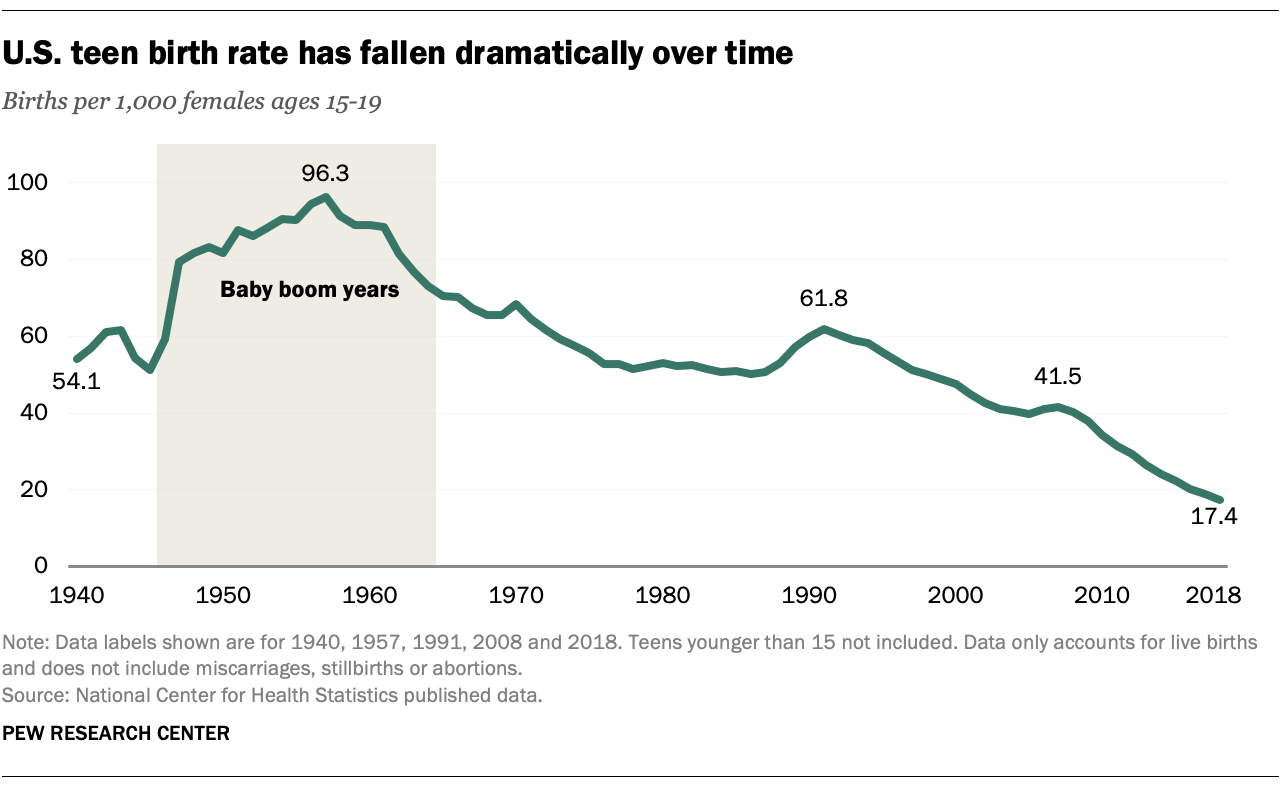
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the teen birth rate in the United States has declined by more than 50% since 1991. In 2020, the teen birth rate was 17.4 births per 1,000 females aged 15-19, down from 27.3 in 2010. However, disparities persist across different demographic groups.
- Racial and Ethnic Disparities: Teen birth rates are significantly higher among certain racial and ethnic groups. In 2020, the teen birth rate was 23.3 per 1,000 among Hispanic females, 26.8 among Black females, and 10.6 among White females.
- Socioeconomic Disparities: Teen pregnancy is also more common among females from low-income families. In 2020, the teen birth rate was 27.6 per 1,000 among females living below the poverty level, compared to 11.8 among females living above the poverty level.
Risk Factors
Numerous factors contribute to the risk of teen pregnancy, including:
- Early sexual initiation: Females who initiate sexual activity at a young age are more likely to become pregnant.
- Lack of access to contraception: Teenagers who do not have access to reliable contraception are more likely to experience unintended pregnancies.
- Peer pressure: Teenagers who have friends or peers who are pregnant are more likely to become pregnant themselves.
- Family instability: Teenagers who come from unstable or dysfunctional families are more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors.
- Mental health issues: Teenagers with mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety, are more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors.
Consequences for the Teenage Mother
Teen pregnancy can have significant consequences for the teenage mother, including:
- Educational attainment: Teen mothers are less likely to complete high school and pursue higher education.
- Economic instability: Teen mothers are more likely to experience poverty and unemployment.
- Health risks: Teen mothers are more likely to experience pregnancy complications, such as premature birth and low birth weight.
- Social isolation: Teen mothers may face stigma and isolation from their peers and community.
Consequences for the Child
Teen pregnancy can also have negative consequences for the child, including:
- Developmental delays: Children born to teenage mothers are more likely to experience developmental delays and learning disabilities.
- Health problems: Children born to teenage mothers are more likely to have health problems, such as asthma and obesity.
- Behavioral problems: Children born to teenage mothers are more likely to exhibit behavioral problems, such as aggression and delinquency.
Prevention and Intervention
Preventing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying risk factors. Effective prevention strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing teenagers with accurate and age-appropriate information about sexual health and contraception.
- Access to contraception: Ensuring that teenagers have access to affordable and reliable contraception.
- Parent-child communication: Encouraging open and honest communication between parents and teenagers about sexual health.
- Peer education programs: Utilizing peer educators to provide support and information to teenagers.
- Community outreach: Engaging community organizations and healthcare providers to provide support and services to teenagers.
Intervention programs for pregnant and parenting teenagers are also crucial. These programs provide support and resources to help teenage mothers navigate the challenges of pregnancy and parenthood. Effective intervention programs include:
- Prenatal care: Providing pregnant teenagers with access to prenatal care and support services.
- Parenting education: Providing teenagers with education and support on parenting skills.
- Vocational training: Helping teenage mothers develop job skills and pursue educational opportunities.
- Housing assistance: Providing housing assistance to teenage mothers who are homeless or at risk of homelessness.
- Mental health services: Providing mental health services to teenage mothers who are struggling with mental health issues.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the United States, particularly among certain demographic groups. Understanding the statistics surrounding teen pregnancy is essential for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. By addressing the underlying risk factors and providing comprehensive support systems, we can help reduce the incidence of teen pregnancy and improve the outcomes for both teenage mothers and their children.