Teen Pregnancy Rates Charts: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
Teen pregnancy remains a significant public health concern, with far-reaching consequences for both the young mothers and their children. Understanding the trends and patterns of teen pregnancy rates is crucial for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. This article presents a comprehensive analysis of teen pregnancy rates charts, examining historical data, geographical variations, and the impact of socioeconomic factors.
Historical Trends
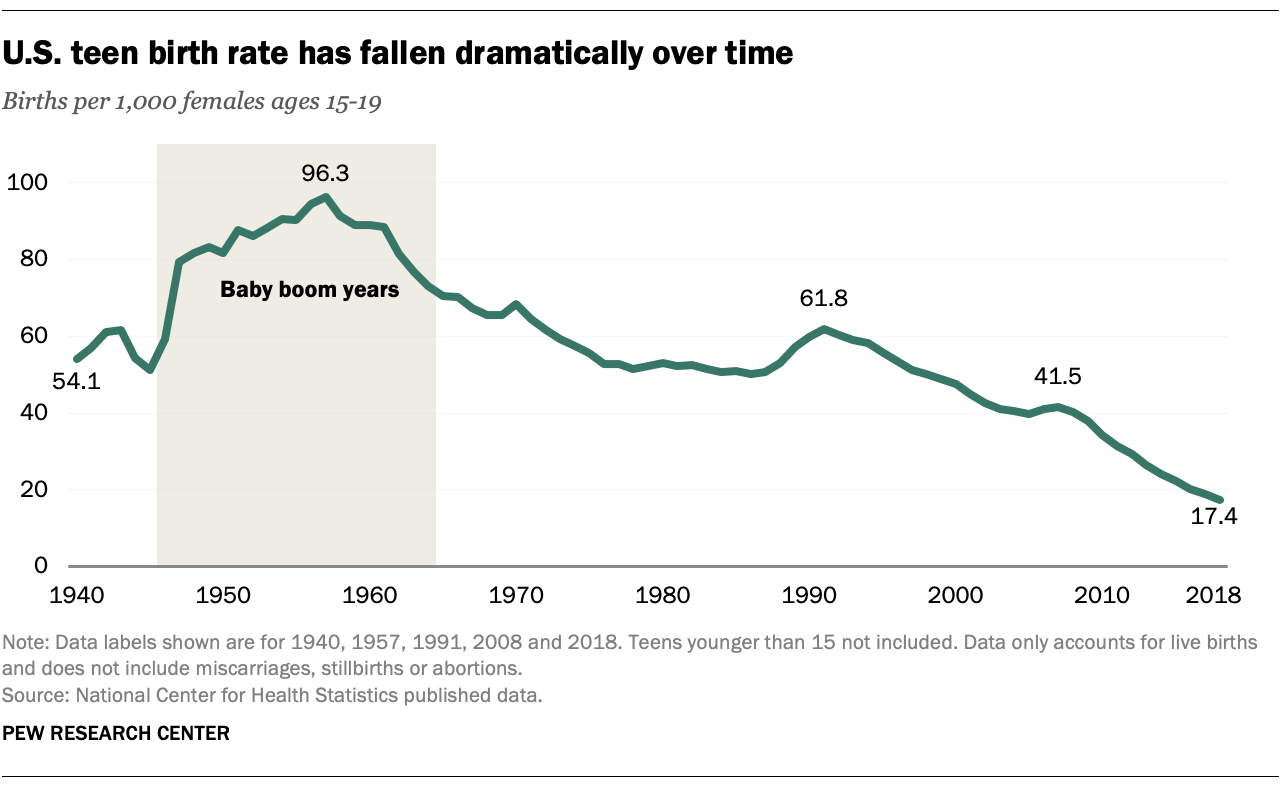
Teen pregnancy rates in the United States have declined significantly over the past several decades. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the teen birth rate fell by 67% between 1991 and 2020, from 61.8 births per 1,000 females aged 15-19 to 19.4 births per 1,000. This decline is attributed to a combination of factors, including increased access to contraception, improved sex education, and delayed sexual initiation.
Geographical Variations
Teen pregnancy rates vary significantly across the United States. In 2020, the highest teen birth rates were observed in the South and Southwest, with states such as Mississippi, Louisiana, and New Mexico having rates above 30 births per 1,000 females aged 15-19. Conversely, the lowest rates were found in the Northeast and West, with states like Massachusetts and California reporting rates below 10 births per 1,000. These geographical disparities are influenced by a complex interplay of socioeconomic, cultural, and policy factors.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic status has a profound impact on teen pregnancy rates. Research consistently shows that young women from low-income families are more likely to become pregnant than their more affluent peers. This disparity is attributed to a number of factors, including limited access to healthcare, inadequate sex education, and a lack of economic opportunities.
Other Risk Factors
In addition to socioeconomic status, other risk factors for teen pregnancy include:
- Early sexual initiation: Young women who begin having sex at a younger age are more likely to become pregnant.
- Lack of contraceptive use: Consistent and correct use of contraception is essential for preventing unintended pregnancy.
- Peer pressure: Teenagers who have friends who are pregnant or who engage in risky sexual behaviors are more likely to become pregnant themselves.
- Mental health issues: Young women with mental health problems, such as depression or anxiety, are more likely to experience unintended pregnancy.
Consequences of Teen Pregnancy
Teen pregnancy has serious consequences for both the young mothers and their children. Young mothers are more likely to drop out of school, have low-paying jobs, and live in poverty. They are also at increased risk for health problems, such as preeclampsia and premature birth. Children born to teen mothers are more likely to have low birth weight, developmental delays, and behavioral problems.
Prevention and Intervention Strategies
Preventing teen pregnancy requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying risk factors and the immediate needs of young women. Effective strategies include:
- Comprehensive sex education: Providing young people with accurate and age-appropriate information about sex, contraception, and healthy relationships is essential for preventing unintended pregnancy.
- Increased access to contraception: Making contraception readily available and affordable for young women is crucial for reducing teen pregnancy rates.
- Economic empowerment: Addressing the socioeconomic factors that contribute to teen pregnancy, such as poverty and lack of opportunity, is essential for long-term prevention.
- Support for young mothers: Providing young mothers with support and resources, such as parenting classes, housing assistance, and job training, can help them overcome the challenges of early motherhood and improve the outcomes for their children.
Conclusion
Teen pregnancy rates charts provide valuable insights into the trends and patterns of teen pregnancy in the United States. Understanding these variations and the underlying risk factors is essential for developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. By addressing the socioeconomic, cultural, and policy factors that contribute to teen pregnancy, we can create a society where all young people have the opportunity to reach their full potential.